What Fields Are There in a Computer Inventory Review
Inventory management is the supervision of noncapitalized avails -- or inventory -- and stock items. Equally a component of supply chain management, inventory management supervises the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and from these facilities to betoken of sale. A key part of inventory management is to proceed a detailed record of each new or returned production equally information technology enters or leaves a warehouse or indicate of auction.
Organizations from small to large businesses can make use of inventory management to track their menses of goods. There are numerous inventory management techniques, and using the right i tin lead to providing the correct appurtenances at the right corporeality, identify and fourth dimension.
Inventory control is a separate area of inventory management that is concerned with minimizing the full cost of inventory, while maximizing the power to provide customers with products in a timely fashion. In some countries, the two terms are used synonymously.
Why is inventory direction important?
Constructive inventory direction enables businesses to remainder the amount of inventory they accept coming in and going out. The better a business organisation controls its inventory, the more money it can relieve in business operations.
A business that has besides much stock has overstock. Overstocked businesses have money tied up in inventory, limiting cash period and potentially creating a upkeep deficit. This overstocked inventory, which is besides called expressionless stock, will often sit in storage, unable to be sold, and eat into a concern's profit margin.
But if a business concern doesn't have plenty inventory, information technology can negatively affect customer service. Lack of inventory means that a business may lose sales. Telling customers they don't have something, and continually backordering items, can cause customers to take their business concern elsewhere.
An inventory management organization can assistance businesses strike the residuum between existence under- and overstocked for optimal efficiency and profitability.
The inventory management process
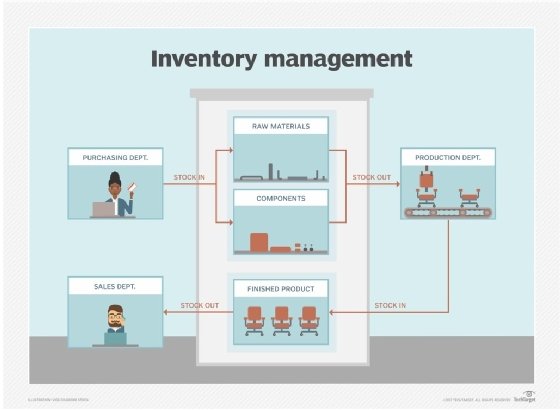
Inventory management is a complex process, particularly for larger organizations, merely the basics are substantially the same, regardless of the organization's size or blazon. In inventory management, goods are delivered in the receiving area of a warehouse -- typically, in the form of raw materials or components -- and are put into stock areas or onto shelves.
Compared to larger organizations with more than concrete space, in smaller companies, the appurtenances may become directly to the stock area instead of a receiving location. If the business concern is a wholesale benefactor, the goods may be finished products, rather than raw materials or components. Unfinished goods are and then pulled from the stock areas and moved to product facilities where they are fabricated into finished goods. The finished goods may be returned to stock areas where they are held prior to shipment, or they may be shipped direct to customers.
Inventory direction uses a variety of data to keep rails of the goods equally they move through the process, including lot numbers, serial numbers, toll of appurtenances, quantity of goods and the dates when they move through the process.
Inventory management systems
Inventory management software systems generally began as simple spreadsheets that track the quantities of goods in a warehouse but have become more circuitous since. Inventory direction software tin now go several layers deep and integrate with bookkeeping and enterprise resources planning (ERP) systems. The systems keep rails of goods in inventory, sometimes beyond several warehouse locations. Inventory management software can as well be used to calculate costs -- often in multiple currencies -- so accounting systems always have an accurate assessment of the value of the goods.
Some inventory management software systems are designed for large enterprises and can exist heavily customized for the detail requirements of an organization. Large systems were traditionally run on premises just are at present also deployed in public deject, private cloud and hybrid cloud environments. Small and midsize companies typically don't demand such complex and costly systems, and they frequently rely on standalone inventory management products, generally through software as a service (SaaS) applications.
Inventory management techniques
Inventory management uses several methodologies to keep the right amount of goods on hand to fulfill customer demand and operate profitably. This task is particularly complex when organizations need to deal with thousands of stock-keeping units (SKUs) that can span multiple warehouses. The methodologies include:
- Stock review, which is the simplest inventory management methodology and is, generally, more highly-seasoned to smaller businesses. Stock review involves a regular assay of stock on mitt versus projected future needs. Information technology primarily uses transmission effort, although there can be automated stock review to define minimum stock levels that then enables regular inventory inspections and reordering of supplies to meet the minimum levels. Stock review tin provide a measure of command over the inventory management process, only it can be labor-intensive and decumbent to errors.
- Just-in-fourth dimension (JIT) methodology, in which products make it every bit they are ordered by customers and is based on analyzing client behavior. This approach involves researching buying patterns, seasonal need and location-based factors that present an accurate flick of which goods are needed at sure times and places. The advantage of JIT is client demand tin be met without needing to keep large quantities of products on hand and in close to existent time. However, the risks include misreading the marketplace demand or having distribution issues with suppliers, which can lead to out-of-stock bug.
- ABC analysis methodology, which classifies inventory into iii categories that represent the inventory values and price significance of the goods. Category A represents high-value and depression-quantity goods, category B represents moderate-value and moderate-quantity goods, and category C represents low-value and high-quantity goods. Each category tin be managed separately by an inventory management arrangement. It'south important to know which items are the best sellers to continue enough buffer stock on paw. For case, more expensive category A items may take longer to sell, only they may not need to be kept in large quantities. One of the advantages of ABC analysis is that it provides meliorate control over high-value goods, simply a disadvantage is that it tin can require a considerable corporeality of resource to continually analyze the inventory levels of all the categories.
- Economical order quantity (EOQ) methodology, in which a formula determines the optimal time to reorder inventory in a warehouse management system. The goal here is to identify the largest number of products to guild at any given fourth dimension. This, in turn, frees upwardly money that would otherwise exist tied upward in excess inventory and minimizes costs.
- Minimum club quantity (MOQ) methodology, in which the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell is adamant. If a business tin can't purchase the minimum, the supplier won't sell it to them. This method benefits suppliers, enabling them to speedily get rid of inventory while weeding out bargain shoppers.
- Commencement in, first out (FIFO) methodology, in which the oldest inventory is sold first to help keep inventory fresh. This is an especially important method for businesses dealing with perishable products that will spoil if they aren't sold within a specific fourth dimension period. It as well prevents items from condign obsolete before a business has the risk to sell them. This typically means keeping older merchandise at the front end of shelves and moving new items to the back.
- Concluding in, showtime out (LIFO) methodology, in which the newest inventory is typically recorded as sold first. This is a adept practice when inflation is an result and prices are ascent. Because the newest inventory has the highest cost of product, selling information technology before older inventory means lower profits and less taxable income. LIFO as well means the lower toll of older products left on the shelves is what'south reported equally inventory. Notwithstanding, this is a difficult technique to put into practice, as older items that sit around have a take a chance of becoming obsolete or perishing.
- Safety stock methodology, in which a business concern sets aside inventory in case of an emergency. The condom stock approach also provides a signal that it'south time to reorder trade before dipping into the safety stock. It's a practiced idea for businesses to work safety stock into their warehouse management strategy in case their supply chain is disrupted.
Inventory direction vs. inventory control
Both inventory direction and inventory control are essential to running a successful direct sales and channel operation. Inventory direction is the overall strategy to ensure adequate inventory, and inventory control encompasses the processes and tools used to track existing inventory. Businesses may cull to use an inventory command system on its own but volition do good from using both together. Here are the essential differences:
Inventory management
Inventory direction is a strategy that ensures businesses e'er take the correct amount of inventory at the right fourth dimension and in the right place. Inventory management tools enable businesses to:
- calculate safety stock;
- calculate reorder points;
- accomplish need planning and forecasting;
- place obsolete items;
- optimize warehouse layout; and
- identify fill rate pct.
Inventory control
Inventory control addresses inventory already in a business's possession. Information technology works at the transactional layer of an ERP arrangement and enables businesses to:
- receive inventory;
- procedure interbranch transfers;
- process receipts;
- pack and ship stock;
- process client invoices; and
- procedure supplier buy orders.
This was final updated in February 2021
Continue Reading Nigh inventory management
- Auto parts maker improves supply chain efficiency with 1 Network
- Discover the core ERP organization components
- What are some reasons to use inventory optimization software?
- IoT'south surprising impact on revolutionizing inventory management
- 6 Inventory Direction Best Practices
Dig Deeper on Supply concatenation and manufacturing
-

need indicate repository (DSR)
-

Top 5 inventory direction techniques
-

Sage cloud ERP services add together production direction module
-

vii supply chain direction primal terms you need to know
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searcherp/definition/inventory-management




Belum ada Komentar untuk "What Fields Are There in a Computer Inventory Review"
Posting Komentar